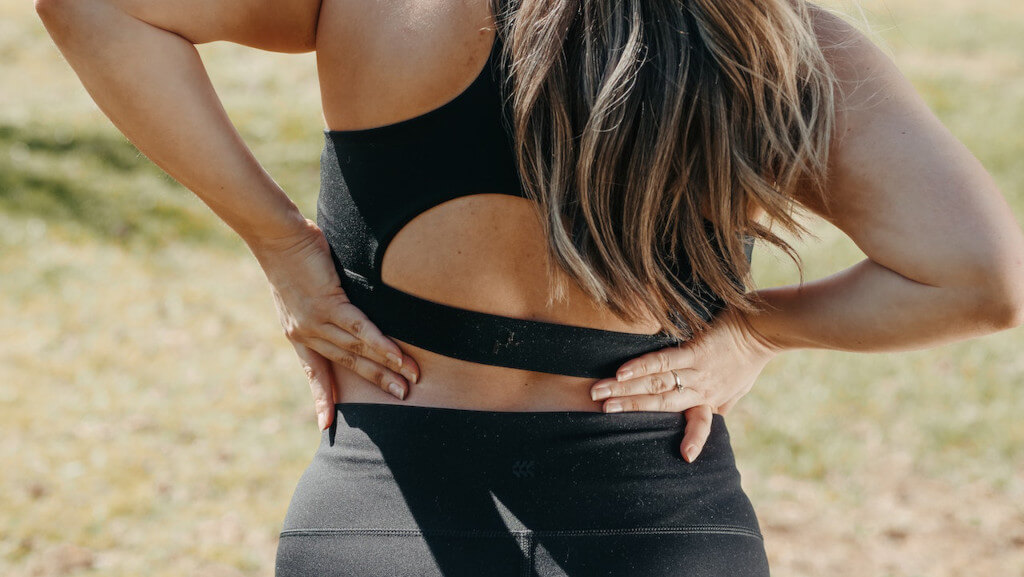
Lower back spasms often cause a great deal of discomfort, but they are entirely treatable. Back spasms can be alleviated or eliminated with the help of specific treatments, stretches, and behavioral adjustments. Spasms in the lower back can come on suddenly, causing pain that is severe enough to be incapacitating. The majority of the time, muscle spasms are brought on by an injury, but having weak back muscles can also put a person at risk of experiencing them.
In this article, we take a look at the various short-term and long-term treatment options for lower back spasms. These treatments include home remedies and strategies for preventing spasms from happening in the first place.
What Does It Feel Like When You Have Spasms in Your Lower Back?
Lower back spasms are caused by the muscles in the back tightening and contracting. The discomfort caused by these contractions can range from barely noticeable to intolerable levels.
When people have muscle spasms, they typically feel them in a particular muscle in their lower back. However, the pain may spread to other parts of the body and cause tension in the muscles that are located nearby. Some suffer from back pain and also have issues with their hips or legs.
Lower back spasms can cause a variety of symptoms, including the following:
- Strain in the area of the lower back.
- After bending over or picking something up, having difficulty moving around.
- Sudden and severe discomfort was felt in the lower back.
- Symptoms include persistent pain in the lower back
- Weakness in the lower back or nearby muscles, such as those in the hips
- A cramping feeling in the back that fluctuates over time
- People who suffer from lower back spasms frequently report that certain activities, such as standing or sitting for extended periods, bring on an increase in the intensity of their pain.
The majority of cases of lower back spasms can be classified as one of two types:
- Acute lower back spasms – Come on suddenly and can be triggered by activities such as lifting heavy objects or changing positions. Acute spasms can result in excruciating pain and make movement difficult or impossible.
- Lower back spasms that are chronic – Occur on a more regular basis and may not appear to be connected to a specific injury. After suffering a back injury, some people go on to develop chronic lower back spasms.
Instant Relief From the Cramping in Your Lower Back
The pain caused by a severe back spasm that comes on all of a sudden can be excruciating. In a similar vein, persistent spasms in the lower back can make it challenging to work or relax.
The following techniques could help provide relief from the pain when it strikes suddenly. These are the following:
Massage
Applying concentrated force to the muscle that’s been affected could help ease muscle tension and put an end to spasms. Applying pressure to the affected region for thirty to sixty seconds, followed by a circular massage of the surrounding area, can help relax spastic muscles.
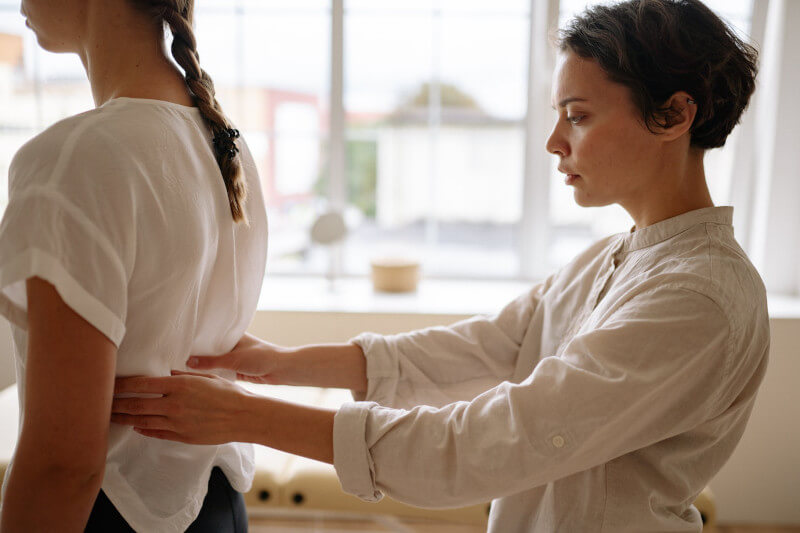

A firm massage might be unpleasant, but it shouldn’t hurt at all. Don’t apply pressure to the area that you are massaging if you can feel a pulse in that area.
Both Heat and Ice
Back pain can be alleviated by using either heat or ice. Both treatments can alleviate muscle tension and reduce inflammation. The use of hot and cold packs in rotation can be of particular assistance.
You could try applying a hot pad for 20 minutes, followed by a cold pad for 20 minutes, with a break of 20 minutes in between each application. It ought to be helpful to use both a bottle of hot water and an ice pack. Don’t apply packs that are either extremely hot or cold to the skin. Wrap them in a towel or a piece of cloth first, then press them against your back.
Muscle Relaxants
When individuals have severe spasms that are noticeable and prominent, a doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants to treat the condition. People shouldn’t use muscle relaxants for longer than three days at a time. Although muscle relaxants may alleviate some of the discomfort associated with back spasms, they don’t address the root cause of the condition.
Hydration
The likelihood of experiencing muscle cramps and spasms is raised when one is dehydrated. Reversing the effects of dehydration and electrolyte loss involves maintaining an appropriate amount of hydration and replacing lost electrolytes.
Utilize a Foam Roller
After working out, a lot of people find that their muscles are tight and tense, so they use foam rollers to help loosen them up. They may also help reduce the severity of muscle spasms that occur in the back. Always consult a medical professional when using a foam roller, as improper use of the tool can result in back injuries.
Reducing the Risk of Lower Back Spasms
When a person has one muscle spasm, they might have a higher chance of experiencing another one in the future. It is important to take care of your back so you can avoid future spasms. Protecting the lower back can be accomplished through the use of the following strategies:
Maintaining proper posture throughout the day includes maintaining proper sitting posture when working for long periods at a desk, sleeping on a bed that is medium-firm and supportive of the spine, and lifting heavy objects with the legs rather than the back.
Medications Available Without a Prescription
Ibuprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like naproxen, are effective in reducing the severity of back pain and inflammation.
Diagnosis
Lower back spasms can be difficult to diagnose, but a medical professional can help. Consult a medical professional as soon as possible if the spasm gets worse or if it does not go away.
A doctor may perform a physical exam, inquire about the patient’s medical history and when the pain first started, inquire about any previous pain the patient has experienced, and perform imaging tests to examine the patient’s muscles and spine, such as X-rays or MRI scans.
People can confuse back spasms with other types of lower back pain. When lower back spasms continue for more than a few days, or when they go away and then come back, it may be the result of a chronic medical condition such as:
- Issues affecting the discs that are supposed to cushion the spinal column
- Narrowing of the spinal column can be caused by osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Fibromyalgia
- Scoliosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- A break in the bone
Back spasms are known to be both incredibly painful and physically crippling. There are, however, a variety of treatment options available to lessen the pain in the short term and address the root causes of muscle spasms. Modifications to one’s lifestyle and activities that build muscle strength can help to protect against muscle spasms, while anti-inflammatory and muscle-relaxing medications can help to reduce the intensity of acute pain. Consult a medical professional to learn the most effective ways to treat both acute and chronic muscle spasms.
